After solar panels, the inverter is the most important component of a solar power system. While solar panels have become very efficient at producing power, the electricity they produce is of the DC variety, while home appliances require AC current to work. The inverter, as its name suggests, converts DC current to AC, which is then fed into your home or to the grid.
But, while there are plenty of inverters out there in the market, solar power systems require a different variety. Besides selecting a good brand, there are at least a few technicalities that buyers should be aware of before making a purchase.
The Solar Inverter in a Nutshell
Unlike regular inverters, solar inverters are grid tied and have something called a Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). The inverter tracks the electricity coming in from the panels, and attempts to hold both the voltage and current at an optimal point.
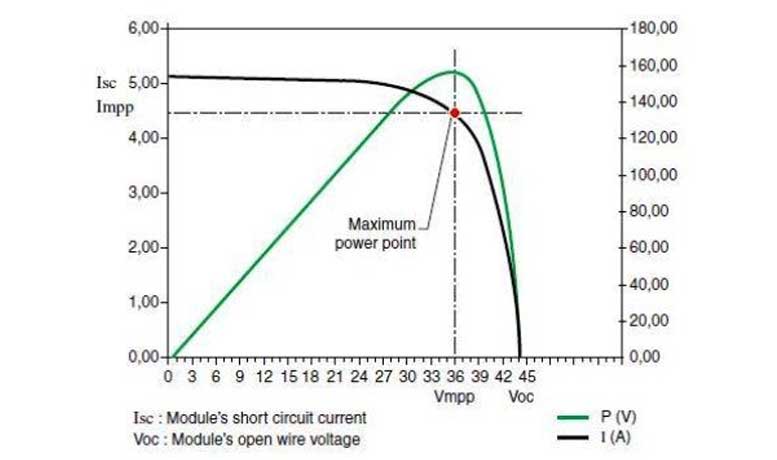
Secondly, solar inverters also need to be selected based on the total size of the PV system. All inverters have a power rating which includes the total DC power they can accept, and the total AC power they can produce based off of it. This is also known as the Inverter Loading Ratio which is basically DC/AC.
Typically, solar installers prefer to oversize a solar power system relative to the inverter. This is done to maximize the inverter’s AC power potential so that no capacity goes to waste. So, if the panels are feeding in less electricity than what the inverter can process (which will happen for most of the day), then less AC current flows through.
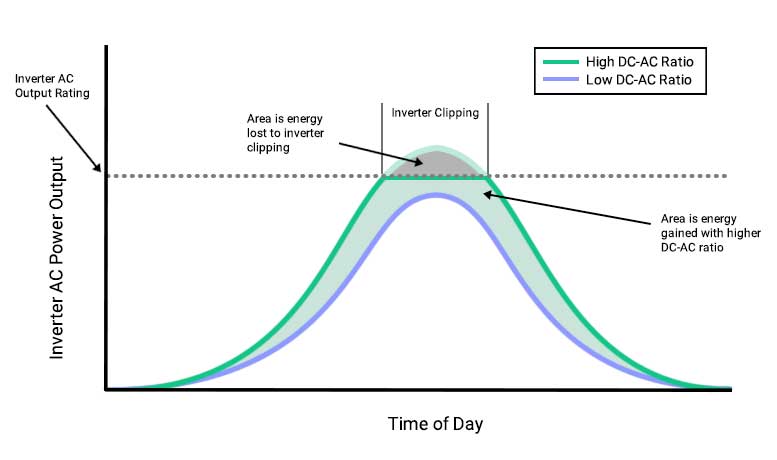
However, the inverter also “clips” any DC power that overshoots its processing limit. This is called inverter clipping, or power limiting. The best designed systems are ones that can keep the inverter working at peak capacity with minimal clipping. A solar installation with a DC/AC ratio of 1.13 to 1.3 are ideal.
The advantage of oversizing a solar power system is that you can capture more energy throughout the day as you have more DC power flowing into the inverter. But, a balanced approach is needed as more DC power also means more of it gets clipped during peak hours.
How to Find the Right Inverter Size for Your Solar Power System
Inverter and system sizing depends as much on your home requirements as it does on the law as well. Firstly, let’s take a look at what’s permitted. The Clean Energy Council’s system design guidelines stipulate under point 9.4:
“In order to facilitate the efficient design of PV systems the inverter nominal AC power output cannot be less than 75% of the array peak power and it shall not be outside the inverter manufacturer’s maximum allowable array size specifications.”
They further illustrate the point with an example of a 2 kWh solar power system against inverters of various specs:
| System 1 | System 2 | System 3 | System 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
a) Proposed array peak power (eg 10 x 200W) |
2000 |
2000 |
2000 |
2000 |
b) 75% of proposed array peak power (Watts) |
1500 |
1500 |
1500 |
1500 |
c) Inverter manufacturers’ maximum allowable array size spec (Watts) |
2100 |
1900 |
2100 |
1900 |
d) Inverter manufacturers’ nominal AC power rating (Watts) |
1700 |
1700 |
1200 |
1200 |
Is manufacturers’ max allowable array size spec greater than array peak power (c>a)? |
YES |
NO |
YES |
NO |
Is inverter nominal AC power greater than 75% of proposed array peak power (d>b) |
YES |
YES |
NO |
NO |
Proposed array peak power – Inverter sizing acceptable |
YES |
NO |
NO |
NO |
Nominal AC power output refers to how much AC electricity the inverter is capable of producing. Maximum allowable array size is essentially how much DC electricity that can flow into the inverter and will be given in your selected inverter’s spec-sheet.
At face value, these rules would make it seem like overclocking or oversizing solar panels relative to the attached inverter is not permitted under the law. But, that’s not entirely true.
The DC input capacity of the inverter indeed needs to be the same as, or, higher than the output of your panels. But, the inverter’s AC output can be 75% (3/4th) of your panel’s DC output.
In other words, we can oversize a PV array by 133% of the inverter’s AC output capacity (1 / [3/4] = 4 / 3 = 1.33) so long as the array’s DC output remains within the inverter’s DC input specs.
Since most states only allow inverters with 5 kW AC output on a residential building, the maximum allowed PV array size here will be 6.65 kW. But, the inverters that will go with such projects will also need to have a DC input capacity of 6.65 kW or more. The same ratio will work for every solar project, so, be sure to double check the numbers with your installer before proceeding.
Let Us Help You Find the Right Solar System Size
While most installers will be aware of the legal requirements they need to work under, some often miss important details. It’s always a good idea to educate yourself on such matters so that you can ask the right questions at the right time.
As Australia’s premier solar search engine, bidmysolar™ can help you find a solar installer right for your needs. Our exhaustive selection process ensures that only the best CEC accredited installers get to bid on your project. We’re also with you every step of the way to make sure your solar project is executed without a hitch.
Interested in finding out more? Check out our section on how we work or contact us if you have any questions.





